A herniated disc or slipped disc is a widespread disease that affects about 5% of all people at least once in their lives. The causes for this are the aging process and wear and tear of the spinal column, which already start from the age of 20. Due to the increasing wear of the outer fiber ring of the intervertebral disc, pieces of tissue can escape into the spinal canal and compress nerves and spinal cord. One-sided physical strain and an unbalanced posture when lifting favor a herniated disc. Those affected experience back pain and possibly numbness in arms and legs.
Often a herniated disc recedes partially or completely on its own or with conservative therapy. A surgical intervention is always indicated when either significant neurological deficits occur or severe pain persists for 6–12 weeks despite medicament administration, physiotherapy and anti-inflammatory injections.
The therapy of choice is a microsurgical minimally invasive operation via a specific tissue-sparing approach and under a high-resolution surgical microscope or with an endoscope. The results of the operation are better with careful indications than with continued conservative therapy, as these two studies * and * show.
At Inselspital, all spinal column operations are performed by a specialized team of experienced surgeons. Minimally invasive and microsurgical techniques, such as operating under a high-resolution microscope, are part of the daily standard in neurosurgery. These techniques allow for a tissue-sparing operation and ensure a faster recovery of the patient.
At Inselspital, specialists from all disciplines work closely together under one roof and coordinate with each other. Thanks to the cooperation of rheumatology, physiotherapy, neurology, neuroradiology, pain center and orthopedics, the optimal treatment strategy can be developed for the patient on an interdisciplinary basis. Complicated cases are discussed in an interdisciplinary board and often operated on jointly by neurosurgeons and orthopedists. In this way, we create the conditions for the best possible treatment for each individual patient.
What is the function of the intervertebral disc?
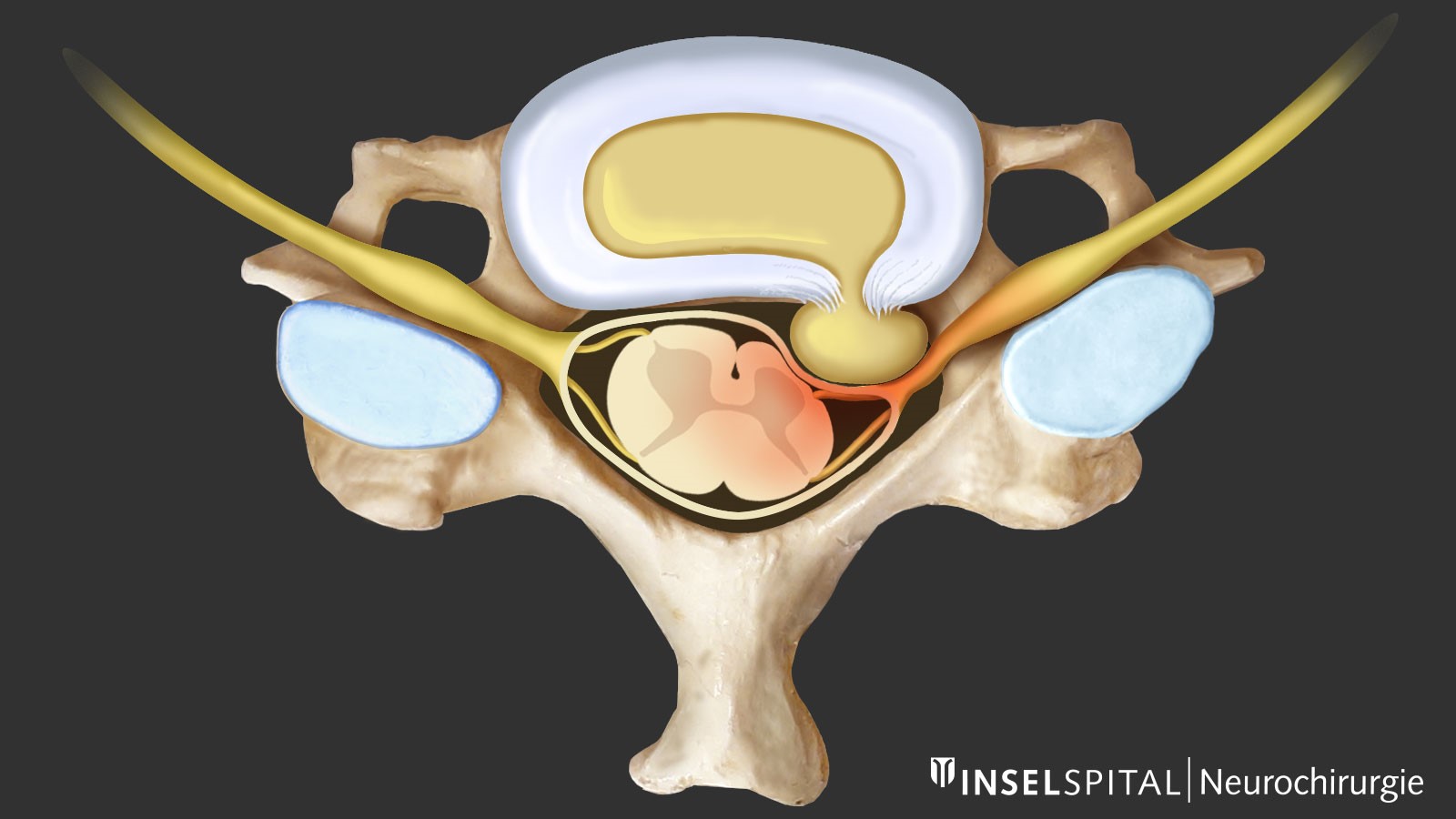
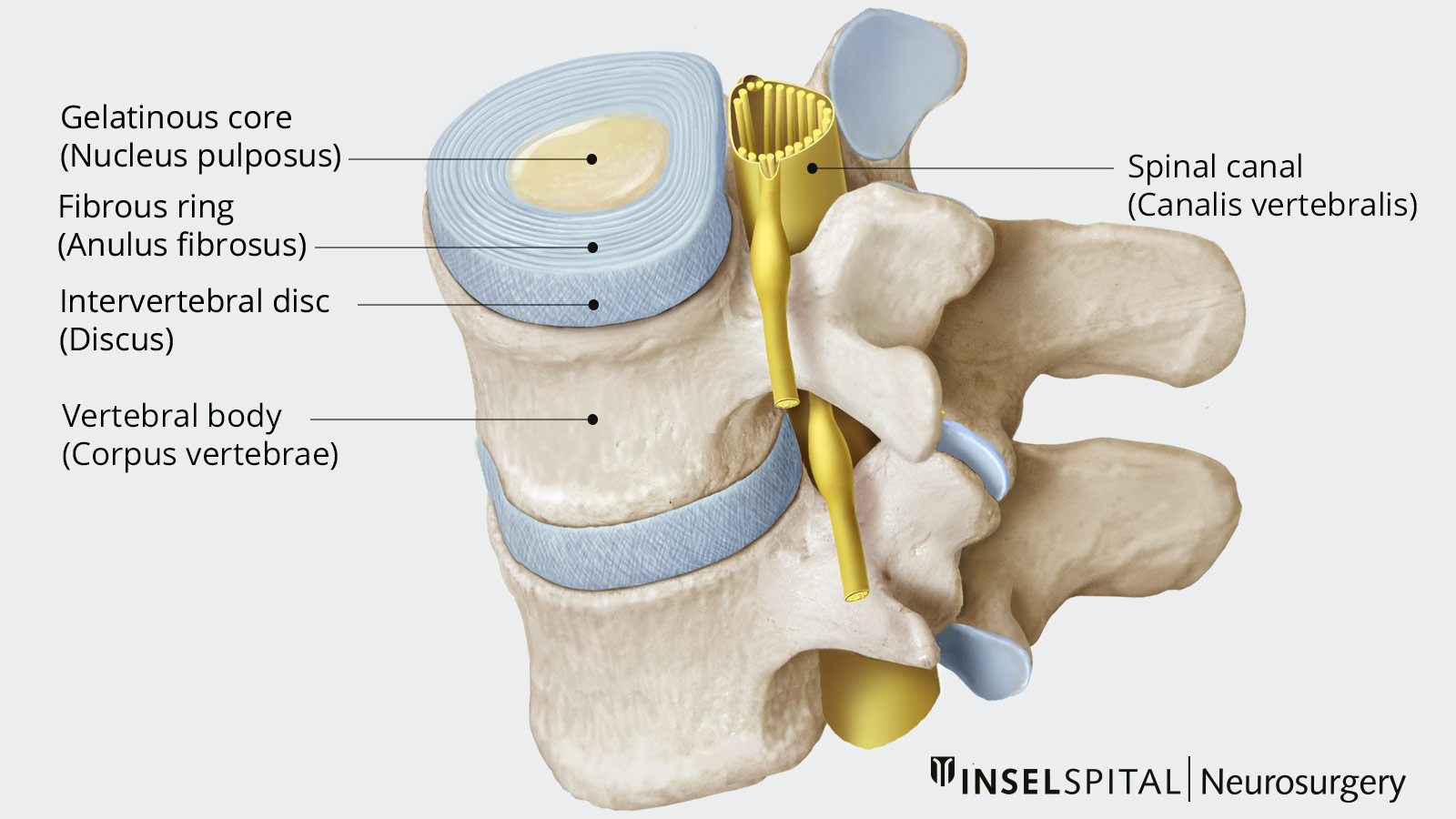
The intervertebral disc is a cartilaginous disc between two adjacent vertebrae and serves as a shock absorber and movement hinge. Humans have 23 intervertebral discs, from the second cervical vertebra to the coccyx. It is only because of the intervertebral discs that the spine can move so flexibly.
An intervertebral disc consists of three parts: a gelatinous inner core (nucleus pulposus), a strong outer fibrocartilage ring (annulus fibrosus) and the cartilaginous parts at the upper and lower ends, which merge into the vertebral bodies. The intervertebral disc distributes the weight that rests on each vertebral body evenly from the upper to the lower vertebral body.
Is a slipped disc a widespread disease?
The price for the mobility and shock-absorbing function of the spine is its wear and tear with increasing age. Over the years, bone thickening, ligament loosening and wear of the intervertebral disc occur. These signs can begin as early as the age of 20 and are accelerated by one-sided strain, incorrect posture when lifting and other factors. Several studies have also shown a genetic predisposition for faster degeneration of the intervertebral disc.
Changes in the spine and protrusions of the intervertebral disc can be detected in the majority of people by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). They usually do not cause any symptoms and therefore have no medical significance. However, about 5% of all people are affected by a slipped disc at least once in their lives. This is why it is a real widespread disease.
What exactly happens with a herniated disc?
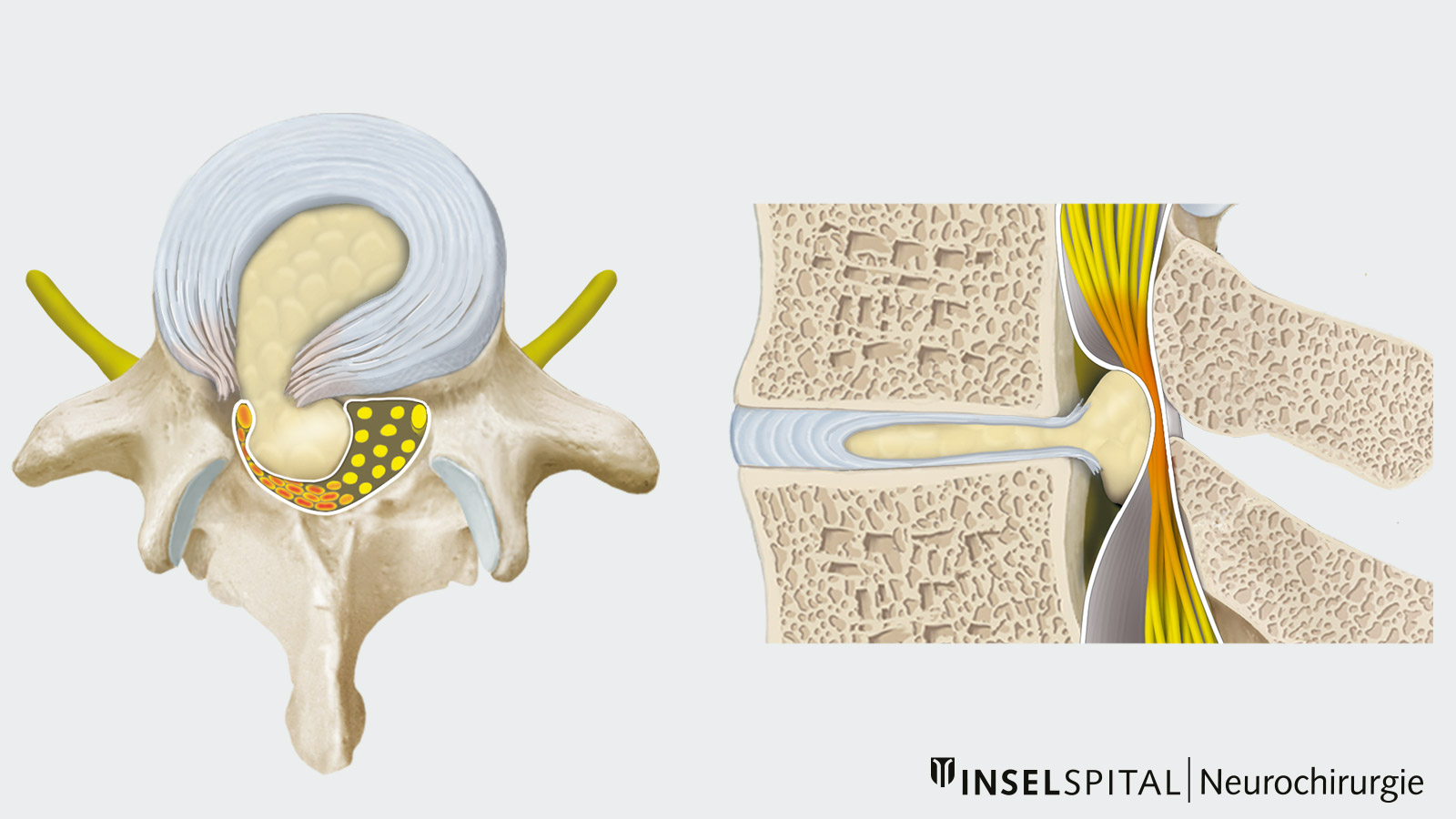
The most common synonyms for a herniated disc are disc hernia, disc herniation, slipped disc or nucleus pulposus prolapse. They all describe this pathological process: Tears in the outer ring of connective tissue, the annulus fibrosus, cause tissue to leak from the inner core of the intervertebral disc, the nucleus pulposus, toward the spinal canal or the nerve roots.
If the tissue is still in contact with the interior of the intervertebral disc and the annulus fibrosus only bulges out, it is called a disc protrusion. A sequestered disc herniation is when the piece of tissue is completely detached from the inside of the disc. This broken-out piece of disc can range in size from a few millimeters to 2 cm. It becomes problematic if the piece of disc exits into the spinal canal and compresses the nerve roots or spinal cord there. Depending on the size and location of the herniation, different symptoms can then occur for lumbar, thoracic oder cervical herniated discs.
When should a herniated disc be operated on?
In cases where surgery is not (yet) necessary, we work closely with the other disciplines of the Back Center at the Inselspital in conservative therapy. These are, for example, rheumatology or our Pain Center. Most disc complaints disappear after a few days to weeks with rest during the acute phase, medication and physiotherapy. However, if the pain does not improve significantly within 6 weeks or if there is severe pain or even a loss of strength, surgical relief should be considered. An absolutely urgent emergency for immediate referral to neurosurgery is when there is a complete loss of strength in a muscle or a bladder emptying dysfunction.
Why you should seek treatment at Inselspital
At our clinic a neurosurgical procedure for a herniated disc is always performed minimally invasive under the operating microscope. There are also more invasive procedures such as the implantation of a prosthesis or a fusion operation, but one should always start with the simplest and gentlest procedure first.
In the neurosurgery department of the Inselspital, disc surgery is one of the most common procedures. You can find more information on the exact therapy plans for the different herniated discs in the individual subchapters.
Further reading
- Adams M, Roughley P. What is Intervertebral Disc Degeneration, and What Causes It?. Spine. 2006;31(18):2151-2161.
- Dowdell J, Erwin M, Choma T, Vaccaro A, Iatridis J, Cho S. Intervertebral Disk Degeneration and Repair. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(3S):S46-S54.
- Miller JAA, Schmatz C, Schultz AB. Lumbar Disc Degeneration. Spine. 1988;13(2):173-178.
- Videman T, Sarna S, Battié M, Koskinen S, Gill K, Paananen H et al. The Long-Term Effects of Physical Loading and Exercise Lifestyles on Back-Related Symptoms, Disability, and Spinal Pathology Among Men. Spine. 1995;20(6):699-709.
-
Lurie J, Tosteson T, Tosteson A, Zhao W, Morgan T, Abdu W et al. Surgical Versus Nonoperative Treatment for Lumbar Disc Herniation. Spine. 2014;39(1):3-16.
-
Bailey C, Rasoulinejad P, Taylor D, Sequeira K, Miller T, Watson J et al. Surgery versus Conservative Care for Persistent Sciatica Lasting 4 to 12 Months. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;382(12):1093-1102.
